Optimization Strategy for the Collaboration of Home Decoration Supply Chain in Hunan, China
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
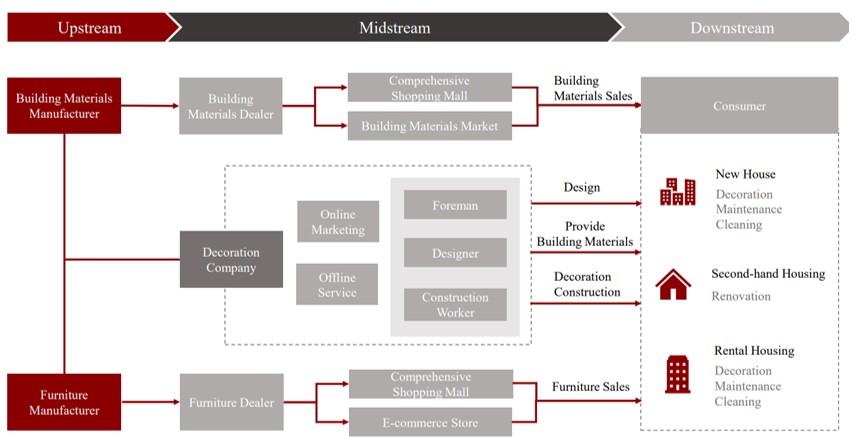
In order to improve the modernization level of the home-decoration industry, this study explored the optimization strategy for the collaboration of supply chain in Hunan China. The research investigated current situation of home decoration in Hunan, and formulated the optimized scheme of collaboration. Previous literature was surveyed, the research method of observation and interview was used to investigate the current situation, and the induction method was used to analyze and summarize the data. Research results show that the cloud system can provide a new model for service providers, a more reasonable resource sharing system between members of the home decoration supply is recommended to build. For business decisions between upstream and downstream members of the supply chain it is highly suggested. The application of cloud system as the platform of home decoration can also reduce the operating costs of suppliers and improve customer satisfaction at the same time.
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความนี้ได้รับการเผยแพร่ภายใต้สัญญาอนุญาต Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ซึ่งอนุญาตให้ผู้อื่นสามารถแชร์บทความได้โดยให้เครดิตผู้เขียนและห้ามนำไปใช้เพื่อการค้าหรือดัดแปลง หากต้องการใช้งานซ้ำในลักษณะอื่น ๆ หรือการเผยแพร่ซ้ำ จำเป็นต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากวารสารเอกสารอ้างอิง
Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. (2020, October 26 to 29). Proposal of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China on Formulating the Fourteenth Five-Year Plan for National Economic and Social Development and Long-term Goals for 2035[Conference session]. 5th Plenary Session of the 19th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, Beijing, China.
Croxton, K. L., García‐Dastugue, S.J., Lambert, D. M., & Rogers, D. S. (2016). The supply chain management processes. International Journal of Logistics Management, 12(2), 13-36.
Emerson, C. J., & Grimm, C. M. (1998). The relative importance of logistics and marketing customer service: a strategic perspective. Journal of Business Logistics, 19(1), 17-32.
Ellram, L. M., Tate, W. L., & Billington, C. (2004). Understanding and managing the services supply chain. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 40(4), 17-32.
iResearch. (2021). Research Report on China's home decoration industry in 2021[2021 China Home Furnishing Industry Research Report]. Global brand insight,35,60-65. https://doi.org/:CNKI:SUN:GJPC.0.2021-35-021.
Lee, H., & Whang, S. (1999). Decentralized multi-echelon supply chains: incentives and information. Management Science, 45(5), 633-640.
Lindner, M., Galan, F., & Chapman, C. (2010, September 1-3). The cloud supply chain: A framework for information, monitoring, accounting, and billing [Paper presentation]. 2nd International ICST Conference on Cloud Computing, Spain.
Lindner, M. A., McDonald, F., & Conway, G. (2011, September 25-30). Understanding Cloud Requirements-A Supply Chain Lifecycle Approach [Paper presentation]. The Second International Conference on Cloud Computing, GRIDS, and Virtualization, Rome, Italy.
Sengupta, K., Heiser, D. R., & Cook, L. S. (2010). Manufacturing and service supply chain performance: a comparative analysis. Journal of Supply Chain Management, 42(4), 4-15. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-493X.2006.00018.x
Scott, C., & Westbrook, R. (1991). New strategic tools for supply chain management. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 21(1), 23-33.
Schrdl, H. (2012, April 2). Adoption of cloud computing in supply chain management solutions: a SCOR-aligned assessment web technologies and applications [Paper presentation]. Proceedings of the 14th international conference on Web Technologies and Applications.
Zhou, L., Zhu, Y., & Lin, Y. (2012) Cloud Supply Chain: A Conceptual Mode [Paper presentation]. International Working Seminar on Production Economics, Innsbruck, Austria.