A study on technical employees' intention to leave a job a case study of X Tire manufacturing company
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
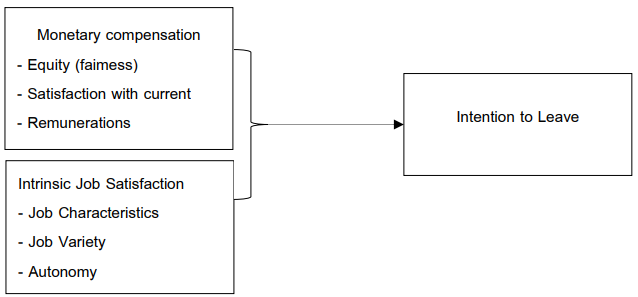
Talent is the most important strategic resource in the development of enterprises, and effective management is the most important thing to enhance the core competitiveness of enterprises. The company should not only focus on recruiting new employees but should explore the real reasons behind the resignation of old employees and find ways to avoid the resignation of skilled employees, which also puts higher requirements on the company's technology accumulation. By collecting and analyzing data through questionnaire survey, this study deeply analyzed the reasons behind the brain drain, and proposed corresponding win-win countermeasures, which not only enabled technical talents to fully enhance their personal value, but also strengthened the company's attraction to employees, retained technical backbone talents, improved the current situation of enterprise talents' turnover intention, and controlled the turnover intention rate of talents. Reduce the impact of skilled employees' turnover intention (work) on enterprise development.
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความนี้ได้รับการเผยแพร่ภายใต้สัญญาอนุญาต Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ซึ่งอนุญาตให้ผู้อื่นสามารถแชร์บทความได้โดยให้เครดิตผู้เขียนและห้ามนำไปใช้เพื่อการค้าหรือดัดแปลง หากต้องการใช้งานซ้ำในลักษณะอื่น ๆ หรือการเผยแพร่ซ้ำ จำเป็นต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากวารสารเอกสารอ้างอิง
Aburumman, O., Salleh, A., Omar, K., & Abadi, M. (2020). The impact of human resource management practices and career
satisfaction on employee’s turnover intention. Management Science Letters, 10(3), 641- 652.
Ahakwa, I., Yang, J., Tackie, E. A., & Atingabili, S. (2021). The influence of employee engagement, work environment and job
satisfaction on organizational commitment and performance of employees: a sampling weight in PLS path modeling.
SEISENSE Journal of Management, 4(3), 34-62.
Ahmad, M. F., Safwan, N. S. Z., Dahlan, N. D., Bakri, N. H. S., Tumijan, W., & Aznan, E. A. M. (2022). Exploring Human Resource
Management Practices and Employability: A Study on Sports Graduates in Malaysia. Hong Kong Journal of Social
Sciences.
Akerlof, G. A. (1982). Labor Contracts as Partial Gift Exchange. Quarterly Journal of Economics, November 1982, 87, 543–69.
Akosile, A. L, & Ekemen, M. A. (2022). The impact of core self-evaluations on job satisfaction and turnover intention among
higher education academic staff: Mediating roles of intrinsic and extrinsic motivation[J]. Behavioral Sciences, 12(7), 236.
Ali, B. J., & Anwar, G. (2021). Employee Turnover Intention and Job Satisfaction. International Journal of Advanced Engineering,
Management and Science, 7(6), 22-30.
Anthony Vandarakis (2020). World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology International Journal of Educational and
Pedagogical Sciences Vol:14, No:11.
Bergmann, T. J., Lester, S.W., De Meuse, K. P., & LGrahn, J. (2000). Integrating the three domains of employee commitment:
an exploratory study. Journal of Applied Business Research, 16(4), 15-26.
Bigliardi, B., Petroni, J. A., & Dormio A. I. (2005). Organizational socialization career aspirations and Intention to Leave (job)
intentions among design engineers. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 26(6), 424-441.
Bulińska-Stangrecka, H., & Bagieńska, A. (2021) The role of employee relations in shaping job satisfaction as an element
promoting positive mental health at work in the era of COVID-19. International Journal of environmental research and
public health.
Chiu, R. K., & Francesco, A. M. (2003). Dispositional traits and Intention to Leave(job)intention. Examining the mediating role of
job satisfaction and affective commitment. International Journal of Manpower, .24(3), 284-298.
Christl, M., De Poli, S., & Figari, F. (2022). Monetary compensation schemes during the COVID-19 pandemic: Implications for
household incomes, liquidity constraints and consumption across the EU[R]. GLO Discussion Paper.
Cloutier, O., Vie, P., Felusiak, L., & Jean, E. (2015). The importance of developing strategies for employee retention. Journal of
Leadership, Accountability & Ethics. 12(2).
Cook. J., & WalL, T. (1980). New work attitude measures of trust, organizational commitment and personal need non- fulfilment.
Journal of Occupational Psychology, (53), 39-52.
Gupta, N., & Shaw, J. (1998). Let the Evidence Speak: Financial Incentives are Effective! Compensation Benefits Review, 30(2),
-32.
Hansen, M., Nohria, N., & Tierney, T. (1999). What’s your strategy for managing knowledge? Harvard Business Review, 106-116.
Heilmann, S.G., Holt, D.T., & Rilovick, C.Y. (2008). Effects of career plateauing on Intention to Leave (job): A test of a model.
Journal of Leadership & OrganizationalStudies,15(1), 5968.doi:10.1177/1548051808317999.
IOSR. (2013). Journal Of Humanities and Social Science (IOSR-JHSS. 14(5). 45-54. e-ISSN: 2279-0837, p-ISSN: 2279-0845.
www.losrjournals.Org
James, B., Madupalli, R., Brian, R., & John, A.W. (2007). The relationship of facets of salesperson job satisfaction with affective
organizational commitment. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 22(5), 311-321.
Kahneman, D. H, Knetsch, J. L., & Thaler, R. H. (1986). Fairness as a Constraint on Profit Seeking: Entitlements in the Market.
American Economic Review, 76, 728–41.
Kalidass, A., & Bahron, A. (2015). The Relationship between Perceived Supervisor Support, Perceived Organizational Support,
Organizational Commitment and Employee Turnover Intention. International Journal of Business Administration, 6(5),1–
https://doi.org/10.5430/ijba.v6n5p82
Konigová, M., & Urbancova, H. (2012). Use of knowledge employees in talent management. Scientia Agriculurae Bohemica,
(1), 39-45.
Law. K.S., Wong, C. S., & Mobley, W. H. (1998). Toward a taxonomy of multidimensional constructs. Academy of Management
Review, .23, 741-755.
Lim, W.D. (2010). A Culture of Work-Life 'Imbalancein Singapore. New Zealand Journal of Asian Studies, 12(2), 22-37.
Lok, P., & Crawford, J. (2004). The effect of organizational culture and leadership style on job satisfaction and organizational
commitment: A cross-national comparison. Journal of Management Development, 23(4), .321-338,2004.
Mathieu. J.E., & Zajac. D. M. (1990). Review and meta-analysis of the antecedents, correlates and consequences of or
zanizational commitment. Psychological Bulletin, (108), 171-194.
Mawardi, M. C. (2022). Alternative Work Arrangements, Work Environment, and Job Stress on Job Satisfaction and Turnover
Intention. Golden Ratio of Human Resource Management, 2(1), 27-39
Meyer, J. P., & Allen, N. J. (1990). The measurement and antecedents of affective, continuance and normative commitment to
the organization. Journal of Occupational Psychology, 63, 1-18. Commitment to the workplace: Theory, research and
application. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Michaud, L. (2000). The value of retaining employees. Agency Sales Magazine, 30(11), 25-27,2000.
Pfeffer, J., & O’ Reilly, C. A. (1987). Hospital demography and turnover among nurses[J]. Industrial Relations. A Journal of
Economy and Society, 26(2): 158-173.
Ramadhani, S. (2014). Factors influencing job satisfaction and turnover intentions in commercial Banks (Doctoral dissertation,
The Open University of Tanzania).
Safwan, N. S. Z., Ahmad, M. F., Bakri, N. H. S., Tajri. A. A., Meor, Ab. Rahim, M. D., Abu Bakar, A. H. & Surat, S. (2023). The
Level of Human Resource Management Practices in Malaysia: A Study on Sports Graduates’ Perceptions. International
Journal of Academic Research in Economics and Management Sciences, 12(1), 157–168.
Shafiq, M. M., & Naseem, M. A. (2011). Association between Reward and Employee motivation: A case study Banking Sector
of Pakistan[J]. Available at SSRN 1857663.
Swailes, S. (2002). Organizational commitment: A critique of the construct and measures. International Journal of Management
Reviews, 4(.2), 155-178.
Tepper, B.J. (2007). Abusive supervision in work organizations: Review, synthesis, and research agenda. Journal of Management,
, 261–289.
Thakre, N., & Shroff, N. (2016). Organizational Climate, Organizational Role Stress and Job Satisfaction Among Employees.
Journal of Psychosocial Research, 11(2), 469–478.
Tomich. A. (2012). The Hudson Report, Employment and HR Trends, Jan-Mar 2012. Hudson http://hudson.sg/Portals/SG/pdf/2012/Hudson%20
Tsai, S. P., Bernacki, E. J., & Lucas, L. J. (1989). A longitudinal method of evaluating employee Intention to Leave (job). Journal
of Business and Psychology. 3(4), .465-473.
Tziner, A., & Birat. A. (1996). Assessing employee Intention to Leave (job) costs: A revised approach. Human Resource
Management Review, 6(2), 113-122.
Williams, M. L., & Dreher, G. F. (1992). Compensation systems attributes and applicant pool characteristics. Academy of
Management Journal,35(3), 571-595.
Winkelhaus, S., Grosse, E. H., & Glock, C. H. (2022). Job satisfaction: An explorative study on work characteristics changes of
employees in Intralogistics 4.0[J]. Journal of Business Logistics, 43(3): 343-367.
Wright, R., & Brehm, S. (1982). Reactance as impression management: A critical review. Journal of Personality and Social
Psychology, 42(ISSUE), 608-618.
Wu, I. H. & Chi, N. W. (2020). The journey to leave: Understanding the roles of perceived ease of movement, proactive personality,
and person-organization fit in overqualified employees' job searching process. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 41(9), 851-870