Performance Evaluation on the Promotion of Rural Health Teaching Strategybased on DEA Analysis in China
Main Article Content
บทคัดย่อ
The urbanization development has resulted in young farmers’ emigration to big cities, and the left middle aged and elderly farmers generally show declining physical and mental functions and are suffering from chronic diseases. Physical health is the major demands of the middle aged and the elderly. To protect the physical and mental health and enhance the quality of life, the government has positively promotion of rural health teaching strategy to reinforce preventive health care, make screening, and manage and prevent chronic
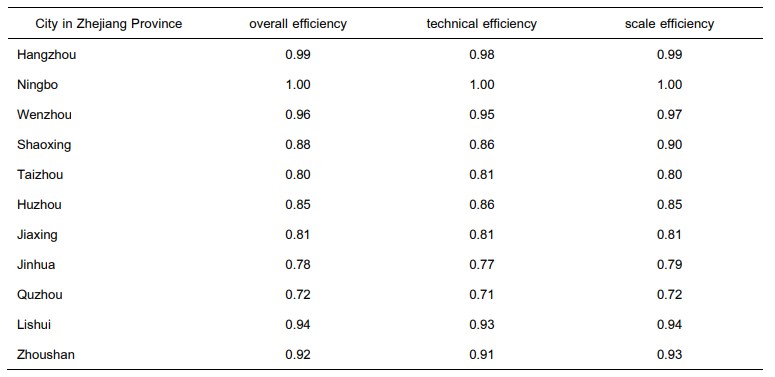
diseases. In this study, Delphi Method is utilized for drafting the performance evaluation indicators for rural health teaching strategy and Data Envelopment Analysis is applied to evaluate efficiency. Taking Zhejiang Province as the research object, cities in Zhejiang Province are selected total 13 DMUs in this study. The research results show that 1. 1 DMU presents strong rural health teaching strategy efficiency, 5 DMUs reveal the rural health teaching strategy practice efficiency in 0.9 and 1, and 7 DMUs appear the rural health teaching strategy practice efficiency lower than 0.9 and 2. the key factors in rural health teaching strategy are found out through sensitivity analysis to understand the sensitivity to efficiency. Finally, suggestions are proposed according to the results, expecting to help farmers present the knowledge and skill about disease prevention and health enhancement so as to promote self-preventive health care and further enhance health quality.
Article Details

อนุญาตภายใต้เงื่อนไข Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
บทความนี้ได้รับการเผยแพร่ภายใต้สัญญาอนุญาต Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) ซึ่งอนุญาตให้ผู้อื่นสามารถแชร์บทความได้โดยให้เครดิตผู้เขียนและห้ามนำไปใช้เพื่อการค้าหรือดัดแปลง หากต้องการใช้งานซ้ำในลักษณะอื่น ๆ หรือการเผยแพร่ซ้ำ จำเป็นต้องได้รับอนุญาตจากวารสารเอกสารอ้างอิง
Bedardb, J. C., Gopi, B. R., & Vijayalakshmi, B. (2015). A multiple criteria model for audit planning decisions, Contemporary Accounting Research, v8, n.1, p.293-308.
Bo, M., Amprino, V., Dalmasso, P., Argentero, P., & Zotti, C. (2015). Written versus verbal information for patients'' teaching strategy on healthcare-associated infections: a cross-sectional study, Journal Of Hospital Infection, v.91, n.4, p.358-361.
Cairney, D. T., & Stewart, E. G. (2015). Audit fees and client industry homogeneity, Auditing: A Journal of Practice & Theory, v.34, n. 4, p.33-57.
Clark, D. B., Tanner-Smith, E. E., & Killingsworth, S. S. (2016). Digital games, design, and learning: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Review of teaching strategical research, 86(1), 79-122.
Fatemeh, B., & Pourmahmoud, J. (2016). A modified SBM-NDEA approach for the efficiency measurement in bank branches. Annals of Operations Research 16(2): 301–326.
Kang, M., Kim, J. W., Lee, H. Y., & Lee, M. G. (2015). Financial statement comparability and audit efficiency: Evidence from South Korea, Applied Economics, Vol. 47, No. 4, 358-373.
Kendrick, D., Maula, A., Reading, R., Hindmarch, P., Coupland, C., Watson, M., & Deave, T. (2015). Risk and protective factors for falls from furniture in young children: multicenter case-control study. JAMA pediatrics, 169(2), 145-153.
Kramlich, D. L., & Dende, D. (2016). Development of a pediatric fall risk and injury reduction program.Pediatric nursing, 42(2), 77.
Ohsatoa, S., & Takahashi, M. (2015). Management efficiency in Japanese regional banks: A network DEA. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 172: 511-518.
Velasco, H. F., Cabral, C. Z., Pinheiro, P. P., Rita de Cassia, S. A., Vitola, L. S., da Costa, M. R., & Amant, S. L. (2015). Use of digital media for the teaching strategy of health professionals in the treatment of childhood asthma.Jornal de Pediatria, 91(2), 183-188.
Von Meyer-Hoefer, M., Von Der Wense, V., & Spiller, A. (2015). Characterising convinced sustainable food consumers. British Food Journal, 117(3), 1082-1104.
Wang, Y- F. (2016). Development and validation of the green food and beverage literacy scale. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 21(1), 20-56.
Wang, Y- F., & Wang, C.- Z. (2016). Do psychological factors affect green food and beverage behavior? An application of the theory of planned behavior. British Food Journal, 118 (9), 2171-2199.
Wu, J. R., Moser, D.K., DeWalt, D. A., Rayens, M.K., & Dracup, K. (2016). Health Literacy Mediates the Relationship Between Age and Health Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. American Heart Association, 9(1), e002250.
Zhou, L., & Zhu, S. (2017). Research on the efficiency of Chinese commercial banks based on undesirable output and super SBM DEA Model. Journal of Mathematical Finance. 7: 102-120